The Evolving Landscape of Sustainable Business: Innovations Driving Environmental Progress
Introduction: Sustainable Business at a Historic Turning Point
By 2026, sustainable business has shifted from a niche concern to a defining force in global markets, reshaping how companies create value, manage risk, and engage with stakeholders across entire value chains. Environmental performance is no longer a peripheral corporate responsibility initiative; it is a core strategic driver influencing capital allocation, supply chain design, product development, and long-term competitiveness. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, this transformation is viewed not as an abstract trend but as an urgent, practical and deeply personal journey that connects boardroom decisions to everyday choices in sustainable living, plastic recycling, and climate-conscious lifestyles.
As regulators, investors, employees, and consumers demand demonstrable progress on climate change, waste reduction, and social impact, the landscape of sustainable business is being defined by innovation, data transparency, and cross-sector collaboration. Advanced technologies, new financial instruments, and circular economy models are converging to support a more resilient and low-carbon global economy. At the same time, organizations are discovering that environmental stewardship and economic performance are increasingly aligned, especially when sustainability is integrated into strategy rather than treated as a compliance obligation. This article explores how the evolving architecture of sustainable business is unfolding, how leading organizations are leveraging innovation to drive environmental progress, and how the insights shared on YouSaveOurWorld.com are helping businesses and individuals navigate this complex transition.
From Compliance to Strategy: The New Business Imperative
The most significant shift in sustainable business over the past decade has been the move from reactive compliance to proactive strategy. Regulatory frameworks such as the European Union's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive and emerging climate disclosure rules from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission are raising the bar on transparency, compelling companies to report on climate risks, emissions, and social impacts in a more standardized and verifiable manner. Organizations that once approached sustainability as a public relations exercise are now integrating environmental metrics into enterprise risk management, capital expenditure planning, and executive remuneration.
This evolution is reinforced by the increasing sophistication of global investors who rely on frameworks such as those developed by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures and the standards of the International Sustainability Standards Board to assess climate risk, resilience and long-term value creation. As a result, sustainability performance is influencing access to capital, cost of borrowing, and valuation multiples. Businesses that embed climate risk analysis into their strategies are better positioned to navigate transition risks, from carbon pricing and evolving regulation to shifting consumer preferences and supply chain disruptions. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, the discussion of sustainable business practices emphasizes this strategic integration, underscoring that sustainability is now a core component of sound business management rather than an optional add-on.
Climate Change as a Strategic and Operational Risk
Climate change is now recognized by major institutions such as the World Economic Forum and World Bank as one of the most significant global risks to economic stability, social cohesion, and long-term prosperity. Rising temperatures, more frequent extreme weather events, and shifting precipitation patterns are disrupting supply chains, damaging infrastructure, and altering resource availability across continents. For businesses, this translates into physical risks to operations, transition risks linked to policy and technology shifts, and reputational risks associated with perceived inaction.
Leading organizations are adopting science-based targets in line with pathways outlined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, committing to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in alignment with global efforts to limit warming to 1.5°C. These commitments require detailed decarbonization roadmaps that address direct operational emissions, purchased energy, and value chain emissions, which are often the largest and most challenging to manage. Businesses are also enhancing climate resilience by stress-testing assets and supply networks against multiple climate scenarios, an approach increasingly reflected in the climate-focused content on YouSaveOurWorld.com, including its dedicated focus on climate change and its implications for global business and society.
Circular Economy and Waste: Redesigning Value Chains
One of the most powerful innovations in sustainable business is the transition from linear "take-make-dispose" models to circular economy systems that prioritize durability, reuse, repair, remanufacturing, and recycling. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation has been instrumental in demonstrating how circular design can decouple economic growth from resource consumption and waste generation, providing businesses with frameworks to redesign products and business models for circularity. This approach is particularly relevant in sectors such as electronics, textiles, packaging, and construction, where material intensity and waste volumes are high.
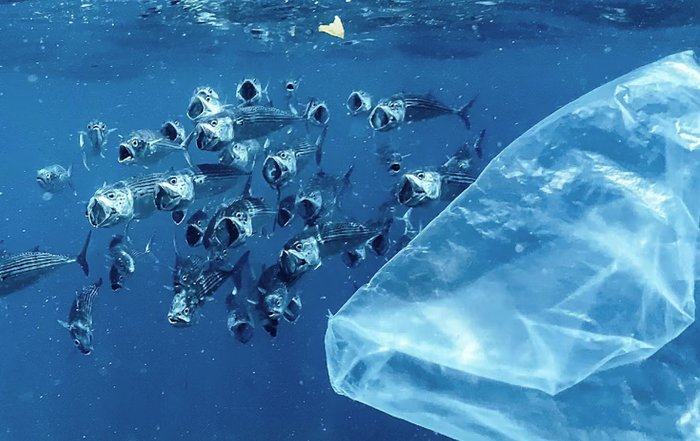
Plastic waste has emerged as a defining circular economy challenge and opportunity. Global initiatives supported by organizations such as the UN Environment Programme are driving efforts to reduce single-use plastics, improve waste management infrastructure, and promote extended producer responsibility schemes. Businesses are experimenting with reusable packaging systems, advanced mechanical and chemical recycling technologies, and bio-based alternatives that can reduce dependency on fossil-fuel-derived plastics. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, the focus on plastic recycling and waste highlights practical strategies for companies and communities seeking to minimize environmental impact while recovering value from materials that were previously discarded.
Technological Innovation: Data, AI, and Clean Energy
Technological innovation is at the heart of the evolving sustainable business landscape, enabling more precise measurement of environmental impacts, more efficient use of resources, and faster scaling of low-carbon solutions. Digital tools such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol-aligned accounting platforms, Internet of Things sensors, and satellite-based monitoring are helping companies track emissions, water use, and land-use change across complex global operations. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being deployed to optimize energy use in buildings, predict equipment failures, and design more efficient logistics networks, thereby reducing emissions and operational costs simultaneously.
In parallel, clean energy technologies have advanced dramatically. The rapid cost declines in solar and wind power, documented by agencies such as the International Renewable Energy Agency, have made renewable energy increasingly competitive with fossil fuels in many markets, while innovations in battery storage and grid management are improving the reliability and flexibility of electricity systems. Corporations are signing long-term power purchase agreements and investing directly in renewable projects, further accelerating the energy transition. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, the intersection of technology, innovation, and sustainability is explored as a critical driver of both environmental progress and business resilience, illustrating how digital and clean energy solutions are reshaping corporate strategies.
Sustainable Design and Product Innovation
Design has emerged as a powerful lever for sustainability, influencing the environmental footprint of products and services throughout their life cycles. From material selection and manufacturing processes to distribution, use, and end-of-life management, design decisions determine energy consumption, emissions, durability, and recyclability. Organizations such as Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Institute and thought leaders in regenerative design are promoting frameworks that encourage designers and engineers to consider circularity, toxicity, and resource efficiency from the earliest stages of product development.
Businesses are increasingly embracing eco-design principles, using tools such as life cycle assessment to compare environmental impacts of different design choices and to prioritize improvements. This shift is visible in sectors ranging from consumer electronics to furniture and building materials, where companies are introducing modular, repairable, and upgradable products that extend useful life and reduce waste. For readers of YouSaveOurWorld.com, the connection between design, sustainability, and innovation is central to understanding how seemingly technical decisions in product development can have far-reaching implications for climate, resource use, and consumer behavior.
Sustainable Finance and the Green Economy
The financial sector has become a powerful catalyst for sustainable business transformation, channeling capital toward low-carbon infrastructure, clean technologies, and socially responsible enterprises. Green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and impact investing strategies are growing rapidly, supported by guidelines from organizations such as the International Capital Market Association and data from providers that specialize in environmental, social, and governance analysis. These instruments align financing conditions with sustainability performance, rewarding companies that achieve measurable improvements in emissions, energy efficiency, and social outcomes.
Central banks and financial regulators, including members of the Network for Greening the Financial System, are examining how climate risks could affect financial stability and are encouraging greater integration of climate considerations into risk management and disclosure practices. This evolving financial architecture is helping to mainstream sustainability in corporate decision-making, as access to capital increasingly depends on credible environmental strategies and transparent reporting. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, the broader economy is analyzed through the lens of this green transition, emphasizing how financial innovation can accelerate environmental progress while supporting long-term economic resilience.
Global Collaboration and Policy Frameworks
Sustainable business does not operate in isolation from global policy frameworks and multilateral efforts. The Paris Agreement, the UN Sustainable Development Goals, and biodiversity commitments under conventions such as the Convention on Biological Diversity provide overarching objectives that guide national policies and corporate strategies alike. As countries update their nationally determined contributions and implement climate and biodiversity policies, businesses are required to adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes, carbon pricing mechanisms, and environmental standards.
International organizations such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and International Energy Agency provide analysis and guidance on policy design, technology pathways, and sectoral decarbonization, helping businesses understand the broader context in which they operate. For a global audience, including readers of the global section of YouSaveOurWorld.com, these frameworks underscore that sustainable business is inherently international, shaped by cross-border supply chains, global markets, and shared environmental challenges that demand coordinated responses.
Corporate Culture, Education, and Environmental Awareness
Behind every sustainable business transformation lies a cultural shift that requires new skills, mindsets, and forms of collaboration. Environmental awareness is no longer confined to specialized sustainability teams; it is becoming a core competency across functions such as finance, procurement, operations, marketing, and product development. Companies are investing in training programs, partnerships with academic institutions, and internal knowledge platforms to build sustainability literacy and empower employees to contribute to environmental goals in their daily work.
Educational institutions and platforms, including leading universities and open learning initiatives such as Coursera, are expanding their offerings in sustainability, climate science, and green innovation, enabling professionals at all levels to deepen their expertise. This emphasis on education and awareness aligns closely with the mission of YouSaveOurWorld.com, whose environmental awareness and education content aims to bridge the gap between high-level policy and corporate strategy on the one hand, and practical knowledge for individuals and communities on the other. By fostering informed, engaged stakeholders, businesses can build internal momentum for change and strengthen their social license to operate.
Lifestyle, Consumer Behavior, and Personal Well-Being
The evolution of sustainable business is deeply intertwined with changes in consumer behavior and lifestyle choices. As awareness of climate risks, biodiversity loss, and pollution grows, individuals are increasingly seeking products and services that align with their values, from low-carbon mobility and plant-based diets to energy-efficient homes and ethically sourced materials. This shift is reinforced by research from organizations such as the World Resources Institute, which highlights the environmental benefits of more sustainable consumption patterns and the role of demand-side changes in achieving climate targets.
Businesses are responding by offering more sustainable options, improving transparency through labeling and certifications, and engaging consumers in initiatives such as take-back schemes, repair services, and sharing platforms. At the same time, there is a growing recognition that sustainability is closely linked to personal well-being, as cleaner air, healthier diets, and access to green spaces contribute to physical and mental health. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, the focus on lifestyle and personal well-being underscores that environmental progress is not only about reducing harm but also about enhancing quality of life, creating a positive narrative that can motivate sustained engagement from consumers and employees alike.
Integrating Sustainability into Core Business Strategy
For sustainable business to drive lasting environmental progress, it must be integrated into the core of corporate strategy rather than treated as a peripheral initiative. This integration involves aligning sustainability goals with business objectives, embedding environmental metrics into performance management systems, and ensuring that sustainability considerations inform decisions about product portfolios, capital investments, mergers and acquisitions, and market expansion. Leading companies are establishing cross-functional governance structures, engaging boards of directors on climate and sustainability issues, and linking executive compensation to measurable environmental outcomes.
This strategic integration also requires a nuanced understanding of trade-offs and synergies. Businesses must evaluate how sustainability initiatives affect cost structures, revenue opportunities, brand equity, and risk profiles, and they must communicate these dynamics clearly to investors, employees, and other stakeholders. On YouSaveOurWorld.com, the business section emphasizes practical frameworks and case-based insights that help organizations translate high-level sustainability ambitions into actionable strategies, reinforcing the message that environmental responsibility and commercial success are increasingly interdependent.
The Role of Innovation Ecosystems and Partnerships
No single company can address the full spectrum of environmental challenges alone, especially when those challenges span entire sectors and value chains. Innovation ecosystems that bring together corporations, startups, research institutions, non-governmental organizations, and policymakers are becoming essential to accelerate the development and deployment of sustainable solutions. Climate tech accelerators, industry coalitions, and pre-competitive collaborations are helping to reduce the costs and risks associated with pioneering new technologies and business models.
Organizations such as Climate-KIC in Europe and various national innovation agencies are supporting experimentation and scaling of solutions ranging from low-carbon materials to nature-based climate solutions. Businesses are also partnering with cities and regional governments to pilot sustainable mobility systems, energy-efficient buildings, and circular economy initiatives that can later be replicated at scale. The emphasis on innovation and technology on YouSaveOurWorld.com reflects this collaborative reality, highlighting that meaningful environmental progress requires open, cross-sector networks rather than isolated efforts.
Looking Ahead: Building a Credible, Trusted Sustainable Future
As the world moves deeper into the 2020s, the credibility and trustworthiness of corporate sustainability efforts are under intense scrutiny. Stakeholders are increasingly alert to the risks of greenwashing and demand robust data, independent verification, and clear evidence of impact. Standards bodies, assurance providers, and regulators are responding by tightening expectations around disclosure, verification, and the use of environmental claims in marketing and investor communications. Businesses that demonstrate genuine experience, expertise, and authoritativeness in sustainability are better placed to earn stakeholder trust and to influence the broader direction of industry and policy.
For YouSaveOurWorld.com, this evolving landscape reinforces the importance of grounded, practical, and forward-looking analysis that connects high-level trends to concrete actions that organizations and individuals can take. Whether exploring the complexities of sustainable business, the urgency of climate change, or the daily practices of sustainable living, the platform is committed to supporting a global audience of leaders, professionals, and citizens who recognize that environmental progress is both a business necessity and a moral imperative. In this sense, the evolving landscape of sustainable business is not merely a story of new technologies and regulations; it is a story of collective responsibility, shared opportunity, and the possibility of building an economy that respects planetary boundaries while enhancing human well-being for generations to come.